Analysis of The National Dental Commission Bill, 2023
BACKGROUND
The National Dental Commission Bill of 2023 aims to update the Dentists Act of 1948, taking into account the advancements made in dental education since that time. The aim of the new legislation is to improve and revitalise the field of dentistry by repealing the Dentists Act of 1948 and dissolving the Dental Council of India.
The Act of 1948 was an overarching legislative framework governing dental education, profession, and ethical conduct in the country. Its primary points included allowing the government authorities to approve the creation of dental colleges, broadening the scope of higher education in this field, and increasing the number of students who could enrol.
This legislation explicitly provided definitions for pivotal roles within the dental domain, namely dental hygienists, mechanics, and dentists. Furthermore, it empowered the designated council to exercise its prerogative in recognising degrees and diplomas in dentistry, facilitating the registration of dental practitioners, and undertaking inspections to ensure compliance with stipulated standards.
This document aims to analyse the timeline of drafting the Bill, its significant highlights, and the areas of discussion surrounding it.
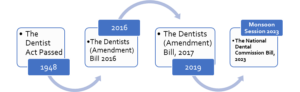
TIMELINE
The National Dental Commission Bill, which was formulated by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in 2020, has been due for almost three parliamentary sessions as it was to be introduced during the Winter Session of 2022. A pre-legislative note was prepared for the subject matter. The proposed Bill will be presented during the Monsoon Session of Parliament to replace the Dentist Act of 1948.
KEY HIGHLIGHTS of the Draft 2023 Bill
- The Dentists Act of 1948 confines its purview solely to the recognition of services and procedures pertaining to tooth restoration or replacement; the newfound Bill encompasses an expanse of oral healthcare services that dentists can efficaciously dispense, augmenting its efficacy manifold.
- The proposed National Dental Commission Bill 2023 endeavours to establish the National Dental Commission (NDC) as the principal entity responsible for regulating dental education practising within the confines of India. The Dental Advisory Council will assist the Commission in doing the same. The composition of the NDC is laid out comprehensively in the proposed Bill wherein 30 individuals, including a chairperson, 7 ex-officio members, and 22 part-time members responsible for carrying out the following functions and responsibilities.
- Chapter II of the proposed legislation makes mention of the several functions of the National Dental Commission wherein Section 10 (2) (c) states that the commission shall articulate policies governing the regulation of dental institutions, dental research facilities, and dental professionals, accompanied by the necessary regulatory framework. Section 10 (2) (g) of the Bill allows NDC to assess the needs of dental healthcare, including the required human resources and healthcare facilities, and develop a plan to meet those requirements.
- In Chapter III of the Bill, the constitution of an advisory body is mentioned, namely the
Dental Advisory Council. This Council will act as the main platform for States and Union territories to voice their opinions and concerns to the Commission regarding dental education and training. It will also assist in shaping the overall agenda, policies, and actions in this area.
- Chapters IV and V of the Bill outline the criteria for administering national entry and exit exams for students who wish to pursue dentistry at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels. These functions will also fall under the purview of the Commission.
- In Chapter VI, the constitution of four Autonomous boards is established. These boards include:
○ Undergraduate Dental Education Board (BDS): To establish the criteria for dental education at the undergraduate level.
○ Post Graduate Dental Education Board (MDS): In order to evaluate the quality of dental education in postgraduate programs, we need to establish specific standards.
○ Dental Assessment & Rating Board: The objective is to establish a procedure for evaluating and grading dental institutions according to the standards set by the Undergraduate Dental Education Board or the Postgraduate Dental Education Board. Additionally, permission will be granted to establish new dental colleges or increase the number of seats available.
○ Ethics & Dental Registration Board: The NDC will oversee the conduct of dental professionals and uphold ethical standards. They will also keep a record of all licensed dentists practising in India.
○ The primary aim of the NDC is to ensure that these boards work in harmony and coordinate effectively to carry out their respective functions.
- Within one year of this Act’s commencement, the State Government is required to take necessary measures to establish a State Dental Council as stipulated in Chapter VII of the Bill. Chapter VIII of the Bill specifies that the Ethics and Dental Registration Board will be responsible for maintaining a National Register for Dentists. This register will be available online and updated in real time. It will include the name, address, and all recognized qualifications of licensed dentists, along with any other details required by regulations.
- While Chapter IX of the proposed legislation outlines policies aimed at maintaining quality and high standards in dental education. It also proposes the implementation of necessary regulations to achieve this goal.
WHAT IS SIGNIFICANT IN THE BILL?
The Bill proposes various changes related to dental education and practice, specifically;
● Implementing Unified Entrance and Exit Examinations for Dental Programs in India
○ Implementing a unified entrance examination, National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET), for securing admission into undergraduate dental programs across all dental institutions in India.
○ Standardising the final year examination, known as the National Exit Test (NEXT), to confer licenses for dental practice in India. The NEXT would serve as a qualifying examination for admission into postgraduate dental programs.
○ Within 3 years from the enactment of this legislation, the National Exit Test will be established, mandating individuals with foreign dental qualifications to complete it to obtain a license to practice dentistry as a dentist and to be enrolled in either the State Register or the National Register.
○ Any person with a foreign dental qualification shall have to qualify National Exit Test (Dental) to obtain a licence to practise dentistry as a dentist and for enrolment in the State Register or the National Register, as the case may be in such a manner as may be specified by regulations.
- Under this Bill, the affiliated institutions can bestow degrees upon deserving candidates. If a candidate, hailing from a non-affiliated college, successfully secures a degree, they shall be eligible to seek recognition for said qualification. Moreover, it encompasses visionary initiatives targeting the cessation of tobacco consumption, galvanising a comprehensive approach to oral well-being.
- The National Dental Commission (NDC) will bring about the harmonisation of objectives and functioning among different Autonomous Boards and State Dental Councils. Undoubtedly, the Bill will enhance the effectiveness of administrative and procedural standards concerning dental care in the nation. Furthermore, as the NDC will have the authority to handle appeals related to relevant issues, it is certain that it will effectively protect the professional ethics of dental practitioners.
- Another key aim of the Bill is to foster a culture of ethical conduct and professional responsibility among dental practitioners, who will be required to provide exemplary care to their patients. The NDC will guarantee the promotion of ethical behaviour and a strong sense of accountability among dental professionals through a comprehensive code of professional conduct. By doing so, it will safeguard the rights and well-being of patients and consumers.
AREAS WHICH REQUIRE FURTHER DELIBERATION
The National Dental Commission Bill 2023 can encounter the following challenges:
- Representation and Autonomy: The Bill raises concerns regarding the significant empowerment of the central government through its authority to appoint the chairperson and ex-officio members of the NDC. Some worry that this heavy reliance on the central government for the selection of all commission members could result in an undue concentration of power and control in the hands of the central government.[1]
- Feasibility and Cost-effectiveness: Establishing a distinct dental commission when a National Medical Commission already exists to oversee a branch of medicine encourages a multilayered bureaucratic system. Creating a new commission, particularly during economic downturns, will have multiple challenges pertaining to adequate resource allocation.
- Lack of attention to Dental Auxiliaries: The Dentist Act of 1948 recognizes two categories of auxiliaries: dental hygienists and dental mechanics. However, the present situation is unfortunate, with only 6,605 dental auxiliaries in India, indicating neglect of these allied health professionals. The current Bill overlooks the crucial role of dental auxiliaries and fails to provide adequate acknowledgement and definition for their role.[2]BENEFITS
The National Dental Commission Bill 2023 is expected to bring some reforms to the stakeholders, including significant improvements in the quality of dental education and practice. They are detailed below:
- Promoting Uniform and Excellent Dental Education: The Bill aims to achieve consistency and excellence in dental education and training nationwide. This will result in the development of highly skilled and proficient dental graduates capable of meeting societal needs and aspirations effectively.
- Fostering Ethical and Professional Dental Care: One of the primary objectives of the Bill is to instil ethical conduct and professional behaviour among dental practitioners. By adhering to a comprehensive code of conduct, dental professionals will ensure the delivery of top-notch care to their patients.
- Encouraging Innovation and Research: The Bill’s positive impact extends to stimulating innovation and research within the dental field. Prioritising research will promote evidence-based practices, elevating the overall quality of dental services.
- Fortifying Dental Education and Practice: With thoughtful provisions, the Bill will strengthen the groundwork of dental education and practice in India. By ensuring standardised and competent dental training, it will enhance the reputation and prominence of the dental profession across the nation.[3]
DISCLAIMER: The opinions expressed herein are entirely those of the author(s). Swaniti makes every effort to use reliable and comprehensive information, but Swaniti does not represent that the contents of the report are accurate or complete. Swaniti is a non-profit, non-partisan group. This document has been prepared without regard to the objectives or opinions of those who may receive it.
[NOTE: This Bill analysis is prepared on the basis of information and materials available in media sources or the
public domain only. ]
[1] What is National Dental Commission Bill 2023, and how it plans to give Indian dentistry a makeover, The Print/ What is National
Dental Commission Bill 2023, and how it plans to give Indian dentistry a makeover (theprint.in)
[2] Indian Dentistry is in Crisis- the New Dental Commission Bill should step up- The Wire Science/ Indian Dentistry Is in Crisis – the New Dental Commission Bill Should Step Up – The Wire Science
[3] Lok Sabha Website, Digital Sansad/ Digital Sansad